JSweet is a Java to JS (JavaScript) translator. It generates significantly less source code than its GWT counterpart, and that source is readable, as you can try out in its sandbox (generally a 1:1 translation). JSweet reads Java source, not class files, facilitating the javac compiler. Essentially it generates TypeScript code, not JS, and uses the TS compiler to generate the final JS output.
JSweet is built component-oriented, that means not only you can write libraries for it (called "candies"), you also can override the way how it generates TypeScript code.
Sounds great! This Blog is about my first steps in trying out JSweet.
Programming languages may have different target domains.
Thus it should not be a problem to emulate JS in Java, right? Just implement a BOM (browser object model) and a DOM (document object model), some kind of AJAX, and provide browser-specific overrides, that should do it.
But what happens in JS when you open a file in Java? A browser doesn't have access to the file system of the client computer! And what happens when you open a Java AWT Frame?
GWT simply does not support these parts of the Java runtime library (rt.jar). Does JSweet?
I downloaded the Quickstart example using git. To transpile the contained sources, Maven (mvn) must be installed. These were my commands:
cd whereverYouTryOutThings
git clone https://github.com/cincheo/jsweet-quickstart.git
cd jsweet-quickstart
mvn generate-sources
The mvn generate-sources command runs the transpilation from Java to JS. This generates a file target/js/quickstart/QuickStart.js, transpiled from src/main/java/quickstart/QuickStart.java. That JS file is referenced in webapp/index.html, and if you load this into a web browser, you will see what QuickStart.java did.
Then I installed the Eclipse plugin, imported the quickstart Maven project, and tried to modify src/main/java/quickstart/QuickStart.java.
package quickstart;
import static def.dom.Globals.document;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class QuickStart
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
final List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("Hello");
list.add("World");
document.getElementById("target").innerHTML = ""+list;
}
}
Mind the ugly access of the public member field innerHTML. That's the way JS does it, and here it invaded Java. Making member fields public is one of the things that you should avoid in OO source code.
The plugin did not generate JS when saving the Java file, so I again had to use the command line to get my changes into JS:
mvn generate-sources
Later I found out that you must activate the plugin for the Eclipse project:
Now every "Save" of a Java file would update the according JS file. Unfortunately not in the target folder but in the js folder, so this plugin is not yet ready, or I missed something.
Transpilation result was the following target/js/quickstart/QuickStart.js. This is already ES6, no more JS, as there is a class definition. The transpiler also can generate ES5, which is closer to JS.
/* Generated from Java with JSweet 2.2.0-SNAPSHOT - http://www.jsweet.org */
var quickstart;
(function (quickstart) {
/**
* This class is used within the webapp/index.html file.
* @class
*/
class QuickStart {
static main(args) {
let list = ([]);
/* add */ (list.push("Hello") > 0);
/* add */ (list.push("World") > 0);
document.getElementById("target").innerHTML = "" + (a => a ? '[' + a.join(', ') + ']' : 'null')(list);
}
}
quickstart.QuickStart = QuickStart;
QuickStart["__class"] = "quickstart.QuickStart";
})(quickstart || (quickstart = {}));
quickstart.QuickStart.main(null);
Lots of boilerplate, as usual in generated code. Mind the last line where quickstart.QuickStart.main(null) gets called. Thus the page that loads the script doesn't need to initialize anything.
Here comes the webapp/index.html page that loads the script:
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
</head>
<body>
<p id="target"></p>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../target/js/quickstart/QuickStart.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
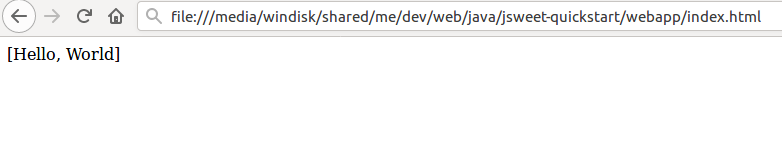
And here is a screenshot of the result:
As you may know, you can not transpile every part of the Java runtime library with GWT. JSweet has similar restrictions, it just uses a fork of the GWT Java emulation library. But it provides a way to enlarge the usable range of the Java runtime: "candies". There are candies (libraries) that refer to Java, and such that refer to JS.
static and public (non-final) in the examples. You will find more conceptual information on the JSweet specification page. If you want to see source code of JSweet, download it from github, it's all open source. There is also a nice video.
I am a little bit frightened by applying the JS style in Java. It took me a long time to understand and use encapsulation in Java, should I give this up now and change to the fragile and error prone JS style?
Nevertheless the possibility to transpile an AWT application to the web is seducing. I will try this out.
ɔ⃝ Fritz Ritzberger, 2018-07-22