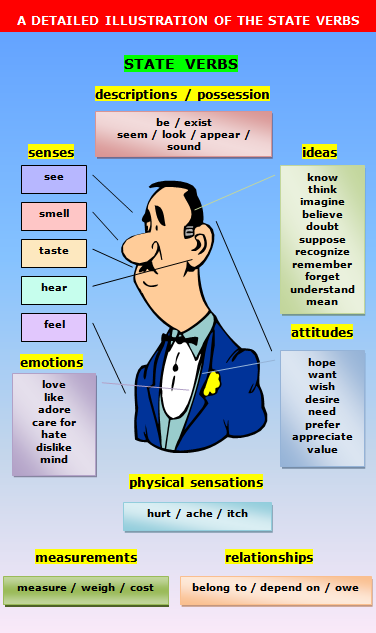
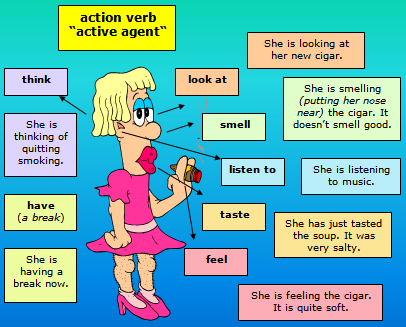
1. Verbs of perceiving:
feel, hear, see, smell, taste,
(look ="seem",appear, sound, seem)
feel, hear, see, smell, taste,
(look ="seem",appear, sound, seem)
State use:
The bag smells of leather.
My pulse feels normal.
The bag smells of leather.
My pulse feels normal.
Action use:
Why are you smelling the bag?
The doctor is feeling my pulse.
Why are you smelling the bag?
The doctor is feeling my pulse.
2. Verbs referring to a state of mind or
feeling:
believe, doubt, forget, hope, imagine, know,
prefer, remember, suppose, understand, want, wish.
adore, desire, detest, dislike, hate, like, love.
believe, doubt, forget, hope, imagine, know,
prefer, remember, suppose, understand, want, wish.
adore, desire, detest, dislike, hate, like, love.
State use:
I hope she'll come soon.
Do you prefer to eat healthy food or fast food?
I remember telling her not to buy it straight away.
I hope she'll come soon.
Do you prefer to eat healthy food or fast food?
I remember telling her not to buy it straight away.
Action use:
We are hoping that she will recover soon. (Present Progressive 2)
More and more people are preferring smaller cars.(Present Progressive 3)
(See The Present.)
We are hoping that she will recover soon. (Present Progressive 2)
More and more people are preferring smaller cars.(Present Progressive 3)
(See The Present.)
3. Verbs referring
to a relationship or a state of being:
be, belong to, consist of, contain, cost, depend, deserve, equal, fit, have, include, involve, matter, owe, own, possess, ...
be, belong to, consist of, contain, cost, depend, deserve, equal, fit, have, include, involve, matter, owe, own, possess, ...